What is Additive Manufacturing?
Additive manufacturing, more commonly known as 3D printing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects from a digital design. Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing, which involves removing material to create a shape (like carving a statue), additive manufacturing builds objects layer by layer, adding material until the final form is complete. This revolutionary approach opens up a world of possibilities for design, production, and customization.
The Expanding Range of Materials
Early 3D printing was largely limited to plastics, but the technology has advanced dramatically. Today, we can 3D print with a vast array of materials, including metals (steel, aluminum, titanium), ceramics, composites, and even living tissues. This broadening material palette allows for the creation of objects with specific properties tailored to their intended function, from lightweight aerospace components to intricate medical implants.

Beyond Prototyping: Additive Manufacturing in Mass Production
For years, 3D printing was primarily viewed as a prototyping tool. Designers could quickly and cheaply create physical models of their ideas before committing to expensive tooling and large-scale production. However, recent advancements have made additive manufacturing increasingly viable for mass production, especially for customized or low-volume products. The ability to produce intricate designs on demand, without the need for complex molds or tooling, is a major advantage.
Customization and Personalization at Scale
One of the most exciting aspects of additive manufacturing is its potential for mass customization. Imagine ordering a pair of shoes perfectly fitted to your feet, a phone case designed to your exact specifications, or a prosthetic limb tailored to your unique anatomy. This level of personalization was previously unimaginable, but 3D printing is making it a reality, shifting the focus from mass production of identical goods to mass production of personalized ones.
Additive Manufacturing’s Impact on Healthcare
The healthcare industry is experiencing a profound transformation thanks to additive manufacturing. 3D printing is used to create custom prosthetics, surgical guides, and anatomical models for planning complex procedures. It’s also being explored for the creation of bio-printed organs and tissues, potentially revolutionizing organ transplantation and regenerative medicine. The ability to create highly customized medical devices offers the potential for improved patient outcomes and more effective treatments.
The Aerospace and Automotive Industries: A New Era of Design
Additive manufacturing is reshaping the aerospace and automotive industries by enabling the creation of lightweight, high-strength components with complex geometries. These components, impossible to manufacture using traditional methods, offer significant advantages in terms of fuel efficiency, performance, and durability. The ability to produce parts on-demand also reduces lead times and inventory costs, further increasing efficiency.
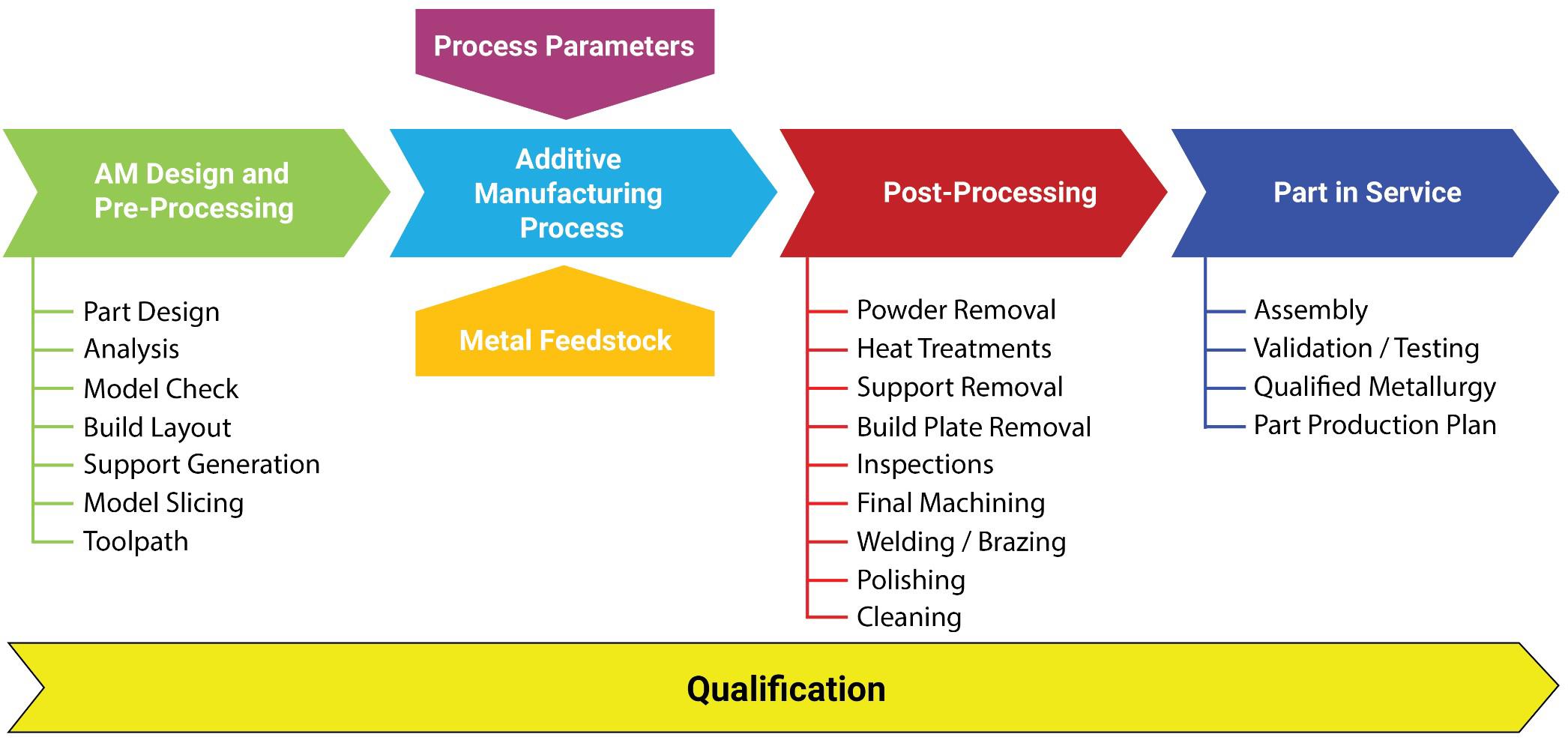
Addressing the Challenges of Additive Manufacturing
Despite its enormous potential, additive manufacturing faces challenges. Scalability for mass production, material costs, and the need for skilled operators are all ongoing concerns. Furthermore, the post-processing steps required for some 3D-printed parts can be time-consuming and expensive. Addressing these challenges will be crucial to unlocking the full potential of this transformative technology.
The Future of Additive Manufacturing: A Collaborative Approach
The future of additive manufacturing likely lies in collaborative efforts across various disciplines. Material scientists, engineers, designers, and software developers need to work together to develop new materials, improve printing processes, and create user-friendly software. Open-source initiatives and industry partnerships are crucial to accelerating innovation and making this technology accessible to a wider range of users and industries. The potential for additive manufacturing to revolutionize how we design, manufacture, and consume goods is immense, and the journey toward realizing that potential is only just beginning.
Sustainability and the Circular Economy
Additive manufacturing offers exciting possibilities for a more sustainable future. By reducing material waste inherent in subtractive manufacturing and enabling the creation of customized, durable products designed for longevity, it contributes to a circular economy. Furthermore, the localized nature of 3D printing can reduce transportation costs and emissions associated with global supply chains.
The Democratization of Manufacturing
One of the most significant impacts of additive manufacturing is the potential to democratize manufacturing. The relatively low barrier to entry for setting up a 3D printing operation empowers small businesses, entrepreneurs, and even individual hobbyists to create and produce their own products. This increased accessibility fosters innovation and empowers a wider range of people to participate in the manufacturing process. Read also about what is additive manufacturing.