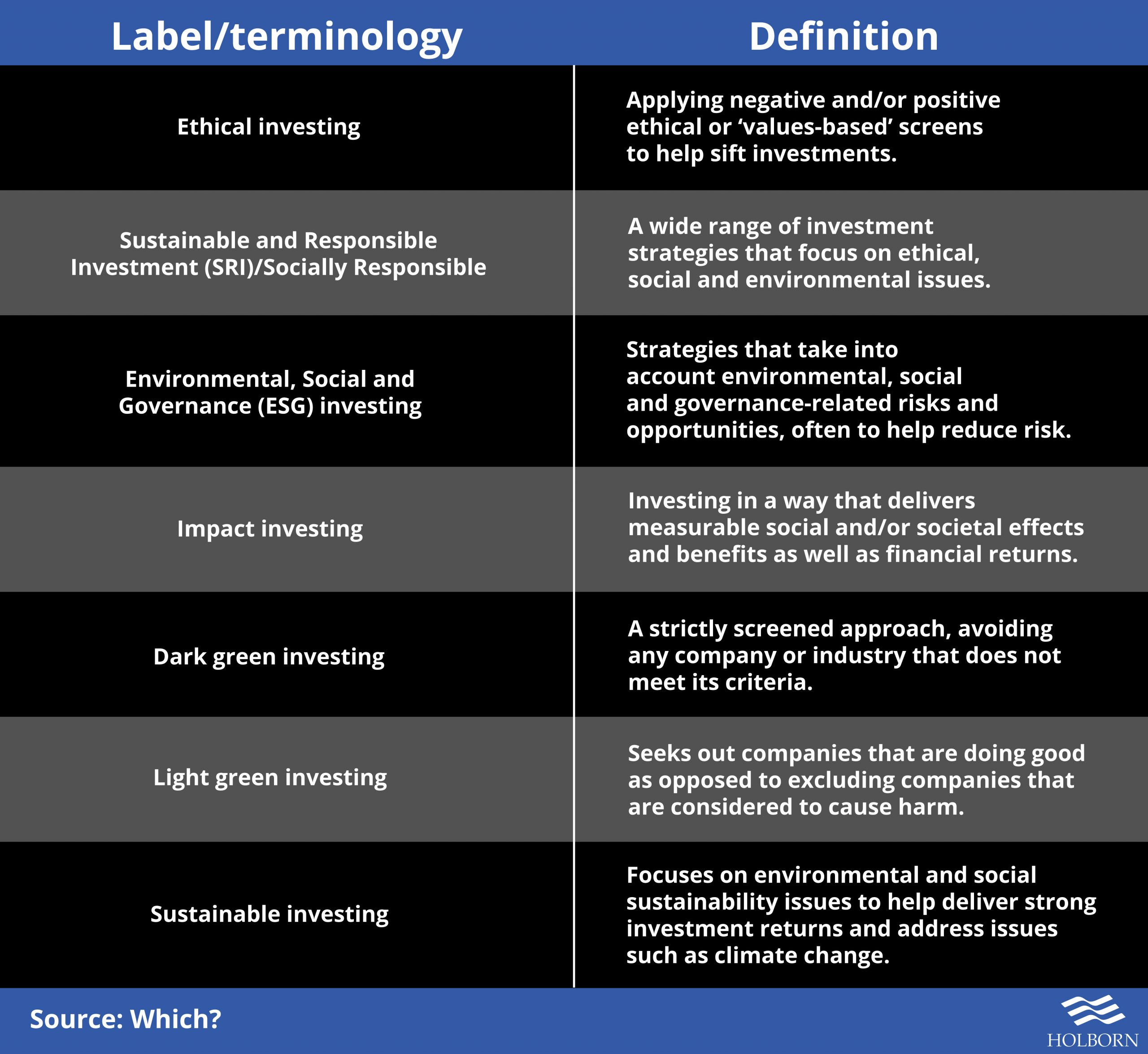
The Expanding Definition of Sustainability
Sustainable investing, once primarily focused on avoiding “sin stocks” like tobacco and fossil fuels, has blossomed into a multifaceted field. Investors now consider a broader range of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. This includes things like a company’s carbon footprint, its treatment of workers, its board diversity, and its overall ethical business practices. The definition of what constitutes a “sustainable” investment is constantly evolving, reflecting growing societal awareness and the increasing availability of data to measure impact.
From Negative Screening to Positive Impact
Early approaches to sustainable investing often involved negative screening – excluding companies involved in activities deemed harmful. While still relevant, the focus has shifted towards positive screening, actively seeking out companies demonstrating strong ESG performance. This includes companies leading in renewable energy, ethical sourcing, or social responsibility initiatives. Investors are increasingly interested in companies that not only minimize harm but actively contribute to positive societal and environmental outcomes.

The Rise of Impact Investing
Impact investing takes this a step further. It’s not just about avoiding harm or choosing good companies; it’s about intentionally investing in ventures with a measurable, positive social or environmental impact. This could involve investing in affordable housing projects, clean energy technologies, or initiatives aimed at improving access to education or healthcare. Impact investors typically seek both financial returns and demonstrable social or environmental benefits, often tracked through rigorous impact measurement and management.
The Growing Importance of Data and Transparency
The credibility and effectiveness of sustainable investing hinge on reliable data. The increasing availability of ESG data, though still imperfect, allows for more informed investment decisions. However, inconsistencies in data collection and reporting methods pose a challenge. The development of standardized reporting frameworks, such as the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) standards and the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) recommendations, is crucial for improving data quality and transparency.
The Integration of ESG into Mainstream Finance
Sustainable investing is no longer a niche strategy. It’s increasingly integrated into mainstream financial decision-making. Many institutional investors, including pension funds and asset managers, are incorporating ESG factors into their investment analysis and portfolio construction. This reflects a growing understanding of the materiality of ESG factors to long-term financial performance and a recognition of the risks associated with ignoring them. For example, climate change poses significant financial risks to companies heavily reliant on fossil fuels.
Addressing Greenwashing and Ensuring Authenticity
With the growing popularity of sustainable investing, concerns about “greenwashing” – the practice of making misleading or unsubstantiated claims about a company’s environmental or social performance – have also increased. Investors are becoming more discerning, demanding greater transparency and evidence-based claims. Third-party verification of ESG data and robust due diligence are vital to ensuring the authenticity of sustainable investment strategies.
The Role of Technology and Innovation
Technology plays a crucial role in advancing sustainable investing. Data analytics tools are helping investors identify companies with strong ESG performance and measure the impact of their investments. Blockchain technology holds promise for enhancing transparency and traceability in supply chains, allowing investors to better assess the social and environmental impacts of their investments. Furthermore, innovative financial instruments, such as green bonds and social impact bonds, are providing new avenues for sustainable investment.
The Future of Sustainable Investing: Collaboration and Regulation
The future of sustainable investing will likely involve greater collaboration among investors, companies, and policymakers. Harmonized global standards for ESG reporting and disclosure are needed to facilitate more informed investment decisions and reduce greenwashing. Regulatory frameworks that incentivize sustainable practices and hold companies accountable for their ESG performance are also crucial. Ultimately, the continued evolution of sustainable investing will depend on a collective commitment to building a more sustainable and equitable future. Read more about the definition of sustainable investing.